BÖNNIGHEIM (aba) Hohenstein has earned accreditation to test cotton for genetically modified organisms (GMOs) according to a new protocol that forms the basis of the Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS) Version 6.0, set for release in March 2020. Hohenstein is one of only a few institutes worldwide to qualify.he new protocol was developed by the International Organisation for Standardisation (ISO) International Workshop Agreement (IWA). The ISO IWA was formed in an effort to implement an official, standardised GMO testing protocol for GOTS certification.
GOTS is an internationally recognised standard for organic, natural fibres. While not all non-GMO cotton is organic, all organic cotton must be free of GMOs to be approved by GOTS. Beginning with GOTS Version 6.0, testing to verify non-GMO seed cotton is required.
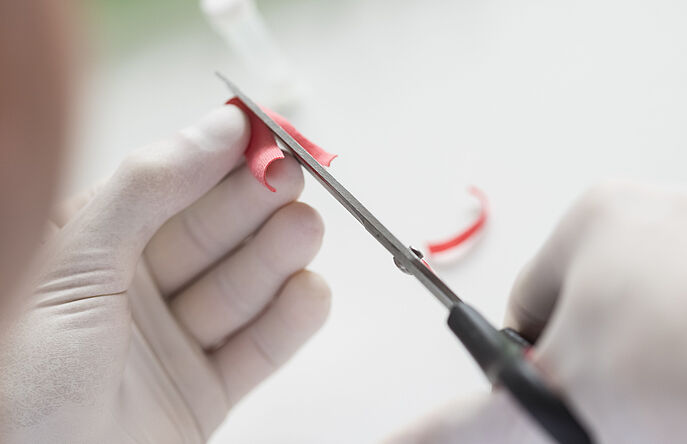
Hohenstein performs the GOTS-approved GMO test by isolating cotton DNA from the undyed product and testing for the worldwide most common cotton lines. A positive test result clearly indicates that genetically modified cotton seeds had been used.
This is one of three methods of testing for GMOs offered by Hohenstein, which has also developed detection methods that can be used on cotton further down the supply chain, including raw fibre, yarn, fabric and finished goods. Hohenstein has been accredited according to ISO 17025 by DAKKS for all three methods. In addition, GMO testing is carried out in accordance with OEKO-TEX® STANDARD 100.
Press Images